The invention and development of GPS date back to 1950s, and the launch of Sputnik which eventually caused the USA to take an active role in researching military satellites. GPS hasn’t always been about helping ordinary people navigate through the city roads or track their vehicles. Its civilian uses were not in the minds of the inventors of GPS back in 1972. But thanks to developers of 612B and the pioneers who opened it to the public, individuals can pinpoint an individual or a vehicle’s location on a given street within 10 feet by using GPS receivers.
Under the direction of Dr Richard Kirschner, the John Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory created the Transit. Transit was built in the late 1950s and it was deployed to the orbit in the 1960s. Transit was the first operational satellite navigation system which included seven polar orbiting satellites. A satellite broadcasted radio signals to the ground stations, which was used to track the location of the satellite. Transit users determined their position on earth by measuring the Doppler shift signals transmitted by the satellites
In the 1960s Dr Ivan Getting, president of the Aerospace Corporation, saw the need for a new satellite-based navigation system. He pictured a global positioning system that would be available anywhere on the planet, 24/7. Getting’s foresight was the reason for gaining Air Force support to form a new satellite navigation program named 621B which later became the GPS. Aerospace began working on Project 621B in the 1960s and successfully launched the first GPS satellites, tested the user equipment, and verified its accuracy under the direction of Bradford W. Parkinson.

Brad Parkinson (centre), Frank Butterfield of The Aerospace Corporation and Cdr. Bill Huston of the U.S. Navy discussing GPS in the early 1970s. A model of a phase-one GPS satellite is on the table at the far right.
In 1972 the first GPS receiver prototype tests took place in White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico. Back then its uses were solely military, guiding planes and bombs to their targets. It wasn’t until 1983 when a Korean airliner was shot down because it strayed into the Soviet territory, that the system was opened for public use. In 1998, Al Gore increased the budget of the project to make it public and more civilian-friendly, since then the use of GPS receivers has skyrocketed and it has been used in vehicles and a variety of technological devices. Today, a vehicle tracker can be used for locating your vehicle anywhere on the planet.
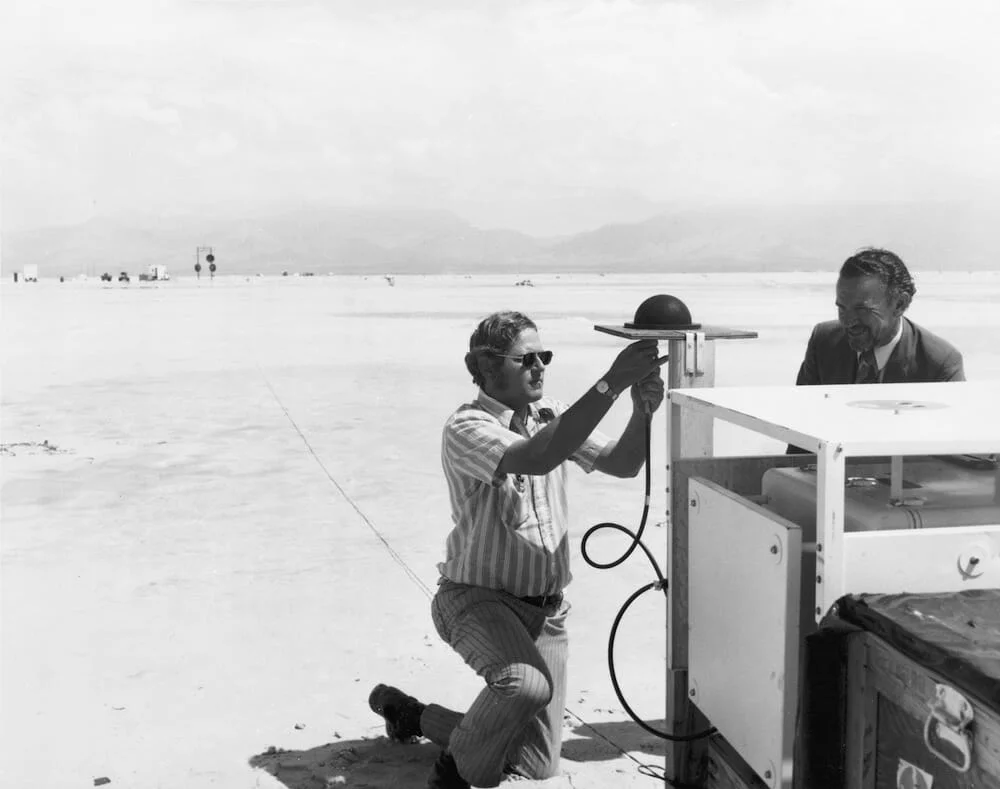

White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico, in 1972 Aerospace Corporation engineer Al Gallegly (left) and Grumman engineer M. Moore testing a transmitter for the 621B system.
This stunning technology has truly revolutionised the way the world functions in the 21st century. On 4 May 1993, Aerospace shared the nation’s most prestigious aeronautical award, the “Collier Trophy” as a member of the GPS team. Dr Ivan Getting’s efforts were awarded in 2002. He shared the “Charles Stark Draper Prize of the National Academy of Engineering” with Bradford Parkinson. Thanks to the vision and extraordinary works of these men, more than 3 billion GPS receivers and tracking devices are being used in vehicles by individuals and corporations in 2017.

A new generation of satellites are being launched to orbit, that promise a great increase to not just the accuracy, but also the availability of GPS. Designated as GPS III, a group of 30 new satellites will replace the currently ageing satellites that have been placed in the orbit in the past 40 years. The highest power and accuracy of GPS Signals means less interference and jamming, and increased accuracy for civilian use of GPS. There are now 3 global satellite systems available for civil use; Galileo in Europe, Globalnaya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya (GNSS) in Russia, and the Global Navigation Satellite systems. NASA is developing specialised GPS receivers for space applications, many of which are already in use.